“Ant Brain Secrets: How the Blood-Brain Barrier Controls Their Colony Roles” 🐜🧠🤯
Hey there, curious minds! Ever wondered how ants know their roles in a colony? It turns out that their brains have a fascinating secret – the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Let’s dive into the surprising discovery that sheds light on ant behavior.
Ants and Their Complex Roles
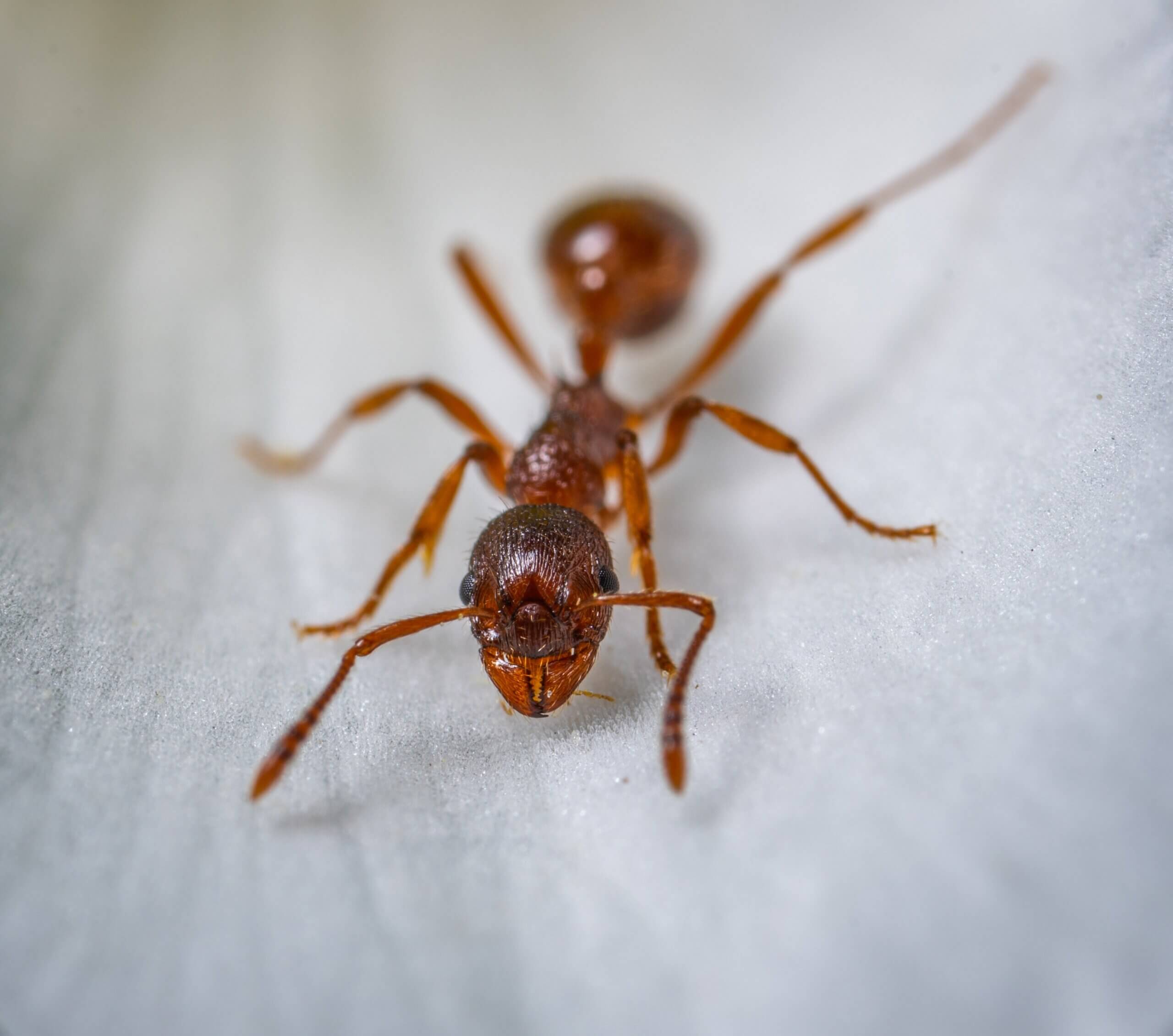
In the world of ants, different members of the colony have different jobs. Some are foragers, while others are soldiers, each playing a crucial role in keeping the colony functioning. But have you ever wondered how ants decide who does what?
The Unexpected Brain Guardian
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania recently made an astonishing discovery. They found that the blood-brain barrier in carpenter ants plays a significant role in controlling ant behavior. But how does it work?
Meet the Hormone Hero
It all comes down to a special enzyme called Juvenile hormone esterase (Jhe), produced by the BBB in ants. This enzyme breaks down Juvenile Hormone (JH3), a hormone known to encourage foraging behavior in ants. Normally, this enzyme is released into the insect’s blood, but in ants, it’s kept inside the BBB cells, controlling the amount of JH3 that enters the worker ant’s brain.
Different Ants, Different Roles
Now, here’s the cool part. The level of the Jhe enzyme in the BBB differs between ants in the same colony. This discrepancy leads to varying levels of JH3 hormone in their brains. And that’s what determines whether an ant becomes a forager or a soldier.
One Protein, Big Impact
This discovery highlights how a single protein, located in the right place at the right time, can influence complex behaviors in ants. It’s not just fascinating for ants; similar mechanisms might also play a role in the behavior of other creatures, like mice.
The Fly Experiment
To test their findings, researchers conducted experiments on fruit flies. They found that when they introduced the ant version of the Jhe enzyme into the BBB of the flies, it changed their behavior, making them more food-seeking, just like foraging ants.
Unlocking the Brain’s Secrets
This research suggests that the BBB plays a significant role in deciding ant roles within a colony. It’s like the brain’s gatekeeper, controlling who becomes a forager and who stays behind to defend the nest.
Beyond Ants
But here’s where it gets even more exciting. The researchers looked into whether similar mechanisms exist in other animals. They found that mouse BBB cells also have enzymes that control hormones, including testosterone. This suggests that this BBB behavior-control mechanism might be more common in the animal kingdom than we thought.
Future Explorations
So, as we learn more about the brain’s secrets, we uncover how complex behaviors in animals are regulated. This research could lead to exciting discoveries about brain functions in various creatures, not just ants. The world of neuroscience is full of surprises! 🌟🧪🐜